UVCBs
15 Complex substances such as slags and drosses – inorganic UVCBs (iUVCBs) – which are generated as by-products from producing and transforming lead are also covered by the Consortium.
This page lists the iUVCBs managed by the Consortium, with links to composition information and infomration from the Lead Registration dossiers published on the ECHA CHEM website.
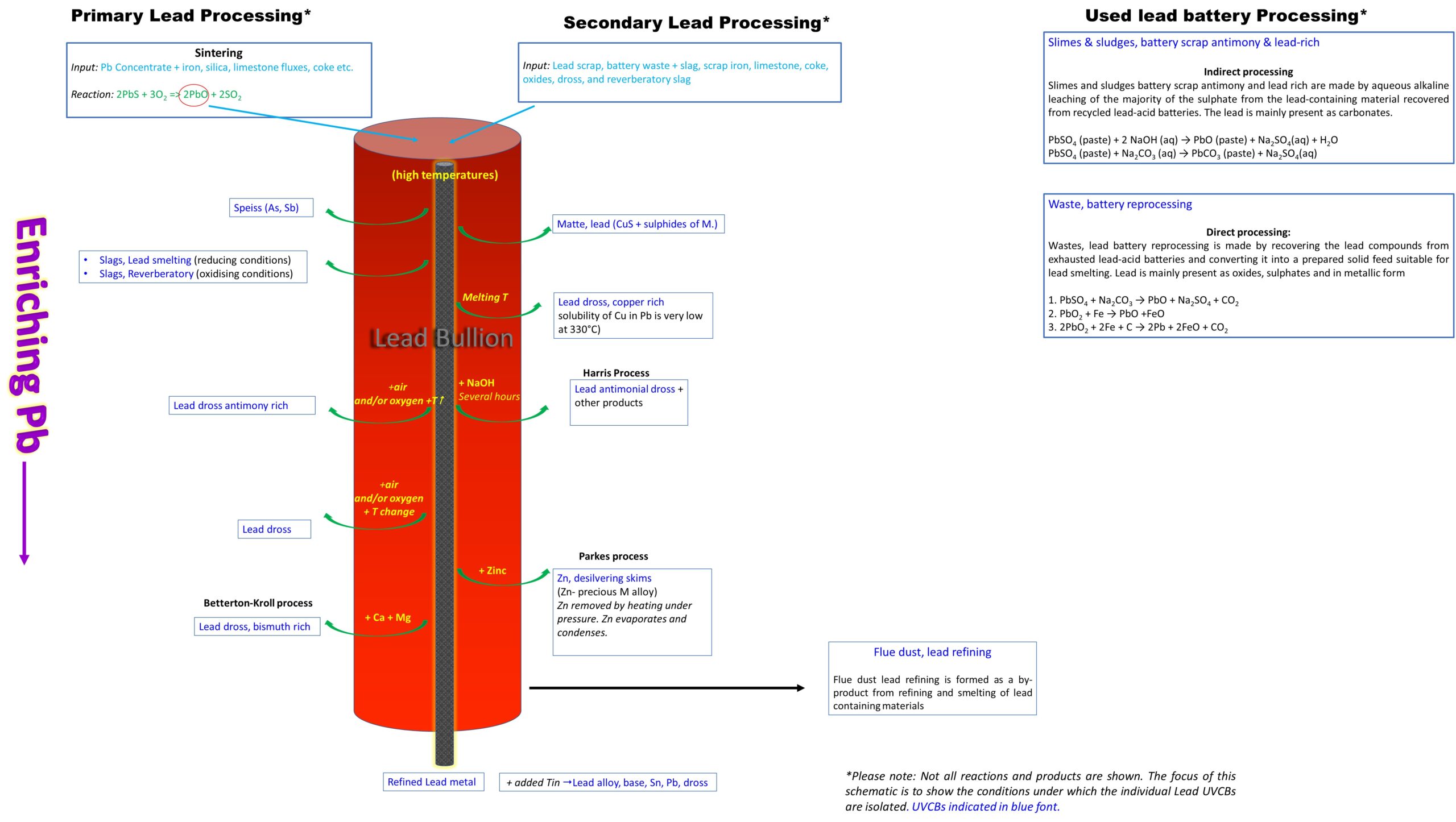
To find out more about the iUVCBs manufactured and used in lead production, click on the process flow chart image to expand a diagram describing the different processes in lead smelting and refining.
Note that the Consortium is currently engaged in a review of substance ID profiles of its UVCB substances. Also note that grade names (e.g. No skin sensitization grade) are historic and may not reflect current classification; the grade names will be amended as part of Lead Registrant dossier updates which will review substance ID, classification, hazard assessment and risk characterisation. Contact the secretariat for more information.
Complex substances
Flue dust, lead refining
(EC 273-809-1)
- New format substance identity profile, substance grade data sheet
- Lead Registration dossier (ECHA CHEM)
Lead alloy, base, Sn, Pb, dross
(EC 273-701-4)
- New format: Substance Identity Profile, Substance grade data sheets:
- Lead Registration dossier (ECHA CHEM)
Lead antimonial dross
(EC 273-795-7)
- New format: Substance Identity Profiles:
- Substance grade data sheets
- Lead Registration dossier (ECHA CHEM)
Lead, Bullion
(EC 308-011-5)
- New format Substance Identity Profiles (SIPs):
- Substance grade data sheets:
- Lead Registration dossier (ECHA CHEM)
Lead dross
(EC 273-796-2)
- New format: Substance Identity Profile, substance grade data sheet
- Lead Registration dossier (ECHA CHEM)
Lead dross antimony rich
(EC 273-791-5)
- Substance grade data sheet: General grade, No skin and eye irritation potential
- Lead Registration dossier (ECHA CHEM)
Lead dross, bismuth rich
(EC 273-792-0)
- New format: Substance Identity Profile, Substance grade data sheet
- Lead Registration dossier (ECHA CHEM)
Lead, dross, copper rich
(EC 273-925-2)
- New format: Substance Identity Profile, Substance grade datasheet
- Lead Registration dossier (ECHA CHEM)
Matte, lead
(EC 282-356-9)
- Substance grade data sheet: General grade, No skin sensitization grade, and Only toxic to the environment grade
- Lead Registration dossier (ECHA CHEM)
Slags, lead reverbatory smelting
(EC 273-800-2)
- New format: Substance Identity Profile, Substance grade data sheet
- Lead Registration dossier (ECHA CHEM)
Slags, Lead smelting
(EC 273-825-9)
- New format: Substance Identity Profile, Substance grade data sheet
- Lead Registration dossier (ECHA CHEM)
Speiss, Lead
(EC 282-366-3)
- New format Substance Identity Profiles (SIPs):
- Substance grade data sheets:
- Lead Registration dossier (ECHA CHEM)
Wastes, lead battery reprocessing
(EC 305-445-7)
- Substance grade data sheet: General grade, No eye damage irritation grade, Lower carc potential
- Lead Registration dossier (ECHA CHEM)
Zinc, desilverising skims
(EC 273-802-3)
- Substance grade data sheet: General grade, Only toxic to the environment
- Lead Registration dossier (ECHA CHEM)
Inactive REACH registrations:
Slimes & sludges, battery scrap antimony & lead-rich
(EC 310-061-8)
- Substance grade data sheet: General grade, Lower carcinogenic potential grade